BMI Calculator | Body Mass Index Calculator
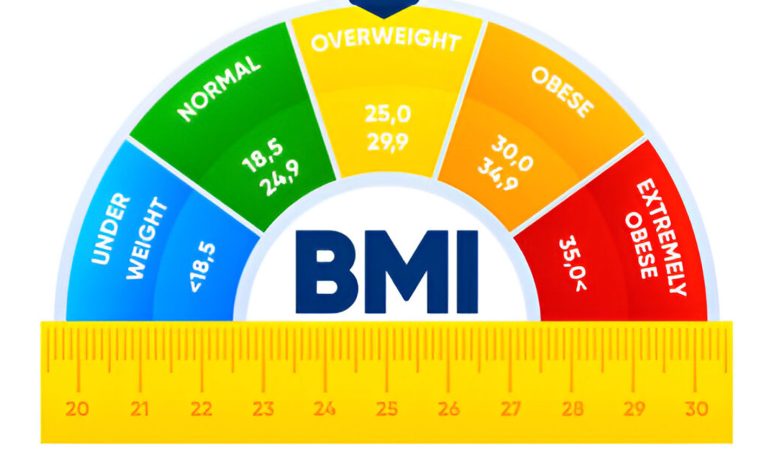

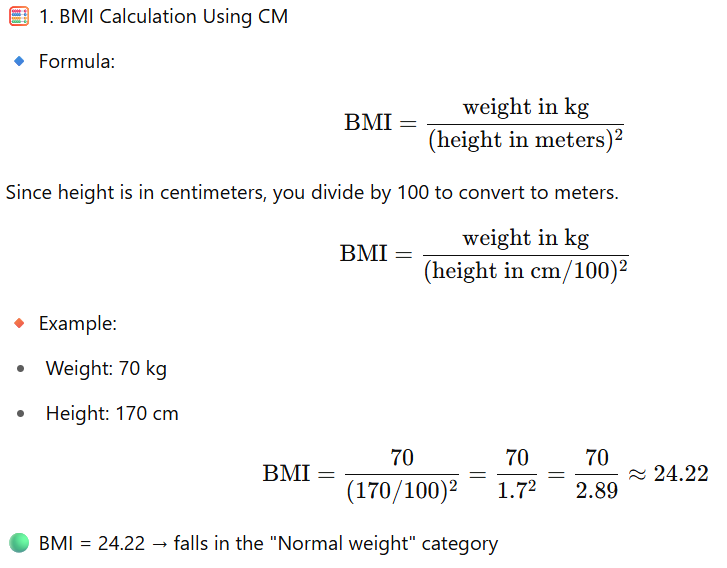
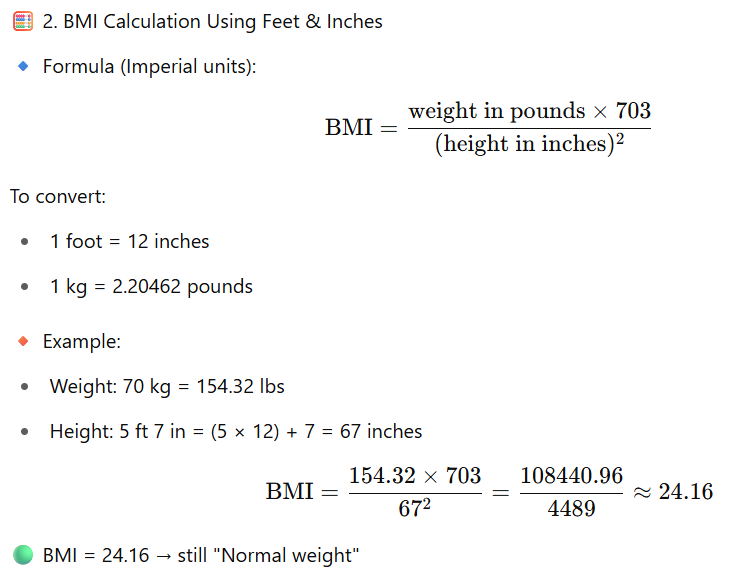
BMI stands for body mass index. It is a number that tells whether your weight is appropriate for your height. BMI tells whether you are overweight, underweight, or have a healthy weight. Your weight (in kilograms) is divided by the square of your height (in metres) to get your BMI.
BMI Calculator
WHO Based BMI Category Chart
| BMI Range (kg/m²) | Category | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 18.5 | Underweight | Possible health risk |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal weight | Healthy weight range |
| 25 – 29.9 | Overweight | Increased health risk |
| 30 – 34.9 | Obesity Class I | High health risk |
| 35 – 39.9 | Obesity Class II | Very high health risk |
| 40 or more | Obesity Class III | Severe health risk |
Why Use the BMI Calculator
Body mass index (BMI) is a simple and effective way to understand whether a person is obese or lean. BMI estimates body fat content based on weight and height. There are many benefits of using it:
BMI tells whether your weight is in a healthy range or not. If BMI is too high, it can be a sign of obesity, which increases the risk of many serious diseases like heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure. At the same time, a very low BMI also indicates weakness and lack of nutrition.
BMI is used by doctors and health experts to understand your health status and give correct advice. It is an easy way to conduct large-scale health surveys and awareness campaigns.
With BMI, you can also monitor your health yourself and make lifestyle changes if needed, such as better eating habits and regular exercise.
Therefore, the use of BMI is very important to control health and adopt a better lifestyle. It not only gives you information about your health, but also helps you move in the right direction.
How to Calculate BMI
To calculate BMI (Body Mass Index), you need a person’s weight and height. The formula varies slightly depending on the units used. Here’s how to do it using:
✅ Height in centimeters (cm)
✅ Height in feet and inches
What are the health risks related to being overweight?
Being overweight is associated with a wide range of health risks. These risks increase as weight increases and are influenced by factors such as body fat distribution, lifestyle, and genetics. Here are the key health risks:
1. Cardiovascular Diseases
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Extra weight increases strain on the heart.
- Heart Disease: Greater risk of coronary artery disease and heart attacks.
- Stroke: Increased chance due to arterial plaque buildup.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Overweight individuals are more likely to develop insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
3. Certain Cancers
Higher risk of:
- Breast (postmenopausal)
- Colorectal
- Endometrial (uterus lining)
- Kidney
- Pancreatic
- Esophageal
4. Joint and Bone Problems
- Osteoarthritis: Stress on joints leads to pain and stiffness.
- Lower back pain: Extra weight burdens the spine.
5. Respiratory Issues
- Sleep Apnea: Fat around the neck can block airways during sleep.
- Asthma: More frequent and severe in overweight individuals.
6. Liver Disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Fat buildup in the liver may cause inflammation.
7. Gallbladder Disease
Higher risk of gallstones due to cholesterol imbalance.
8. Digestive Problems
Increased likelihood of acid reflux and other gastrointestinal issues.
9. Reproductive and Sexual Health Issues
- Infertility: Hormonal imbalances in women.
- Erectile dysfunction: More common in overweight men.
10. Mental Health Conditions
Higher rates of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
11. Reduced Life Expectancy
Severe overweight, especially with abdominal fat, may shorten lifespan.



